Consumer Group
This section describes the definition, model relationship, internal attributes, and behavior constraints of consumer groups in Apache RocketMQ. This topic also provides version compatibility information and usage notes for consumer groups.
Definition
A consumer group is a load balancing group that contains consumers that use the same consumption behaviors in Apache RocketMQ.
Unlike consumers that are running entities, consumer groups are logical resources. Apache RocketMQ initializes multiple consumers in a consumer group to achieve the scaling of consumption performance and high availability disaster recovery.
In a consumer group, consumers consume messages based on the consumption behaviors and load balancing policy that are defined in the group. The following section describes the consumption behaviors that are defined:
Subscription: Apache RocketMQ manages and traces subscriptions based on consumer groups. For more information, see Subscriptions. aa
Delivery order: The Apache RocketMQ broker delivers messages to consumers by using ordered delivery or concurrent delivery. You can configure the delivery method in the consumer group. For more information, see fifo messages.
Consumption retry policy: the retry policy that is used when a consumer fails to consume a message. The policy includes the number of retries and the setting of dead-letter queues. For more information, see Consumption retry.
Model relationship
The following figure shows the position of consumer groups in the domain model of Apache RocketMQ.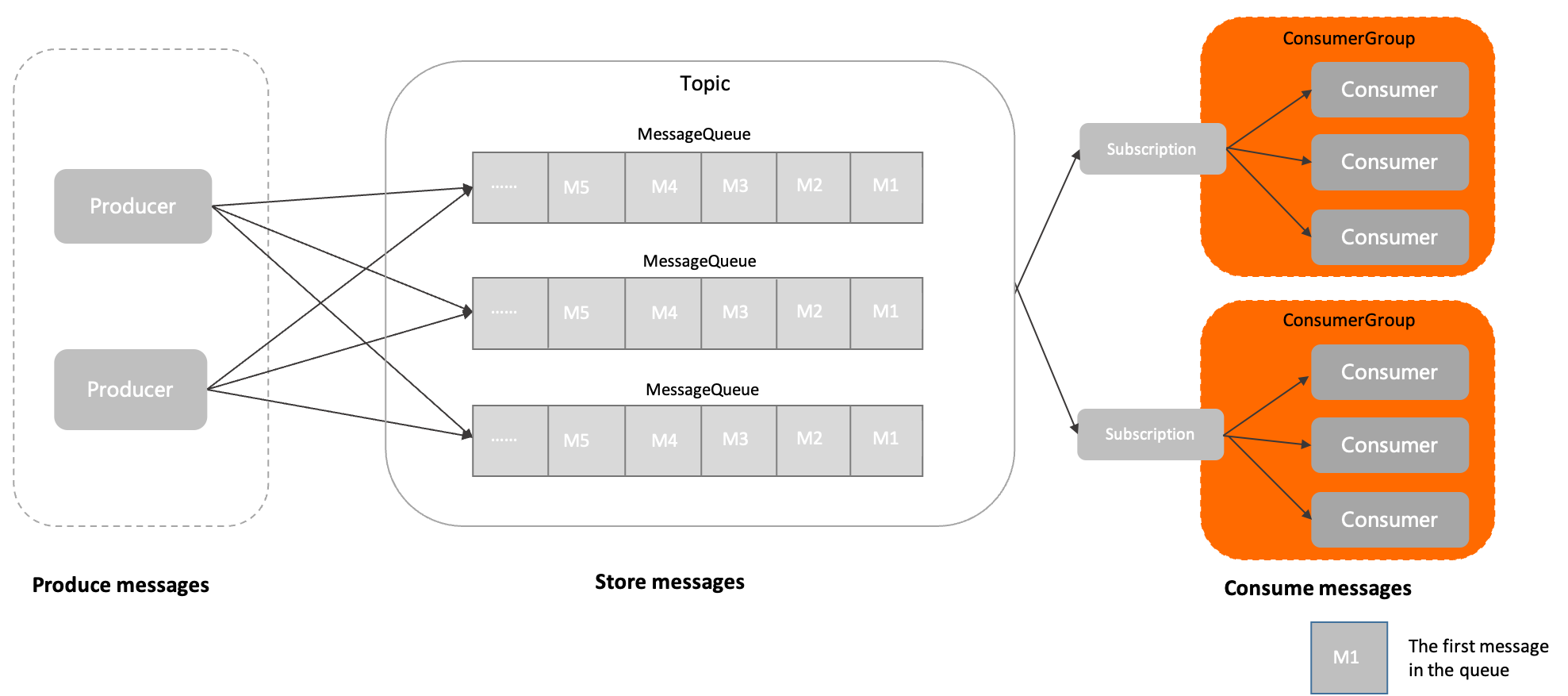
The message is initialized by the producer and sent to the Apache RocketMQ server.
Messages are stored in the specified queue of the topic in the order in which they arrive at the Apache RocketMQ server.
The consumer obtains and consumes messages from the Apache RocketMQ server based on the specified subscription relationship.
Internal attributes
Consumer group name
Definition: the name of a consumer group. Consumer group names are used to distinguish between consumer groups. Consumer group names are globally unique in a cluster.
Values: created and configured by users. For more information, see Parameter limits.
Delivery order
Definition: the order in which Apache RocketMQ delivers messages to a consumer client.
Apache RocketMQ supports ordered delivery and concurrent delivery based on different consumption scenarios. For more information, see Fifo messages.
- Values: The default delivery method is concurrent delivery.
Consumption retry policy
Definition: the retry policy that is used when a consumer fails to consume a message. If a consumer fails to consume a message, the system re-delivers the failed message to the consumer for re-consumption based on the policy. For more information, see Consumption retry.
Values:A consumption retry policy contains the following items:
Maximum retries: the maximum number of times that a message can be re-delivered. If a message fails to be consumed and the maximum number of retries is exceeded, the message is delivered to the dead-letter queue or is discarded.
Retry interval: the interval between which the Apache RocketMQ broker re-delivers a failed message.
For more information about the valid values and default values of maximum retries and retry intervals, see Parameter limits.
- Constraint: Retry interval is available only for push consumers.
Subscription
- Definition: the set of subscription relationships that are associated with the current consumer group. A subscription includes the topics to which the consumers subscribe and the message filter rules that are used by consumers. For more information, see Subscriptions.
Consumers dynamically register subscriptions for consumer groups. The Apache RocketMQ broker persists subscriptions and matches the subscriptions to the consumption progress of messages.
Behavior constraints
In the Apache RocketMQ domain model, consumer management is implemented through consumer grouping, and consumers in the same group share messages for consumption. Therefore, to ensure the normal load and consumption of messages in a group, Apache RocketMQ require all consumers in the same group to keep the following consumption behaviors consistent:
Delivery Order
Consumption retry policy
Version compatibility
As described in Behavior Constraints, the delivery order and consumption retry policy of all consumers in the same group need to be consistent.
Apache RocketMQ server version 5.x: The consumption behavior of the preceding consumers is obtained from the associated consumer groups. Therefore, the consumption behavior of all consumers in the same group must be consistent, and the client does not need to pay attention to it.
Apache RocketMQ server version 3.x/ 4.x history: The preceding consumption logic is defined by the consumer client interface. Therefore, you must ensure that the consumption behavior of consumers in the same group is consistent when you set the consumer client.
If you use the Apache RocketMQ server version 5.x and the client uses the previous version SDK, the consumer's consumption logic is subject to the settings of the consumer client interface.
Usage notes
Create consumer groups based on your business requirements
In Apache RocketMQ, consumers and topics are in a many-to-many mapping relationship. We recommend that you take note of the following rules before you create consumer groups:
Consistent message delivery order: The message delivery order must be consistent for all consumers in a consumer group. The delivery method is either ordered delivery or concurrent delivery. We recommend that you do not use the same consumer group for different business scenarios.
Consistent business type: A consumer group corresponds to a topic. Different business domains have different requirements for message consumption, such as message filter rules and consumption retry policies. We recommend that you use different consumer groups in different business domains. We also recommend that you add up to 10 topics in a consumer group.
Avoid using automated mechanisms to manage consumer groups
In the Apache RocketMQ architecture, consumer groups are logical resources that are used to manage the status of consumers. Each consumer group is associated with various data, such as consumption status, accumulated messages, observable metrics, and monitoring data. We recommend that you strictly manage your consumer groups. Proceed with caution when you add, delete, modify, or query consumption groups.
Apache RocketMQ provides the automatic consumer group creation feature. However, if you enable this feature in production environments, a large number of consumer groups may be created. A large number of consumer groups can be difficult to manage and reclaim and results in the waste of system resources. Therefore, we recommend that you use this feature in only test environments.